Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Nanjing University, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Nanjing, China
2 Nanjing University, School of Electronic Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing, China
3 Nanjing University, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, Nanjing, China
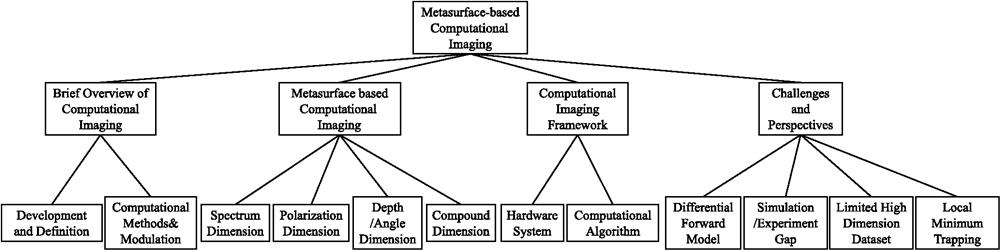
Metasurface-based imaging has attracted considerable attention owing to its compactness, multifunctionality, and subwavelength coding capability. With the integration of computational imaging techniques, researchers have actively explored the extended capabilities of metasurfaces, enabling a wide range of imaging methods. We present an overview of the recent progress in metasurface-based imaging techniques, focusing on the perspective of computational imaging. Specifically, we categorize and review existing metasurface-based imaging into three main groups, including (i) conventional metasurface design employing canonical methods, (ii) computation introduced independently in either the imaging process or postprocessing, and (iii) an end-to-end computation-optimized imaging system based upon metasurfaces. We highlight the advantages and challenges associated with each computational metasurface-based imaging technique and discuss the potential and future prospects of the computational boosted metaimager.
metasurface computational imaging inverse problem algorithm Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 014002
1 中国科学院 微电子研究所, 北京 100029
2 中国科学院 抗辐照器件技术重点实验室,
3 中国科学院 抗辐照器件技术重点实验室, 北京 100029
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 10004
集成电路产业的不断发展以及行业对高能效的不断追求使得工艺尺寸不断缩小, 越来越多的电路工作在亚阈值区, 工艺参数波动导致电路延时呈现非高斯分布。统计静态时序分析作为先进工艺下用于分析时序的新手段, 采用将工艺参数和延时用随机变量表示的方法, 可以加速时序收敛, 显示预期成品率。文章主要研究了亚阈值电路单元延时波动的统计建模方法。分别对单时序弧和多时序弧的蒙特卡洛金标准数据进行建模研究。提出了单时序弧单元延时的分布拟合统计建模方法, 其误差小于6.30%。提出了多时序弧单元延时人工神经网络统计建模方法, 其误差小于4.95%。
亚阈值 单元延时统计建模 波动性建模 分布拟合 主成分分析 人工神经网络 机器学习 sub-threshold cell delay statistic modeling fluctuation modeling distribution fitting principal component analysis artificial neural network machine learning

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing 210093, China
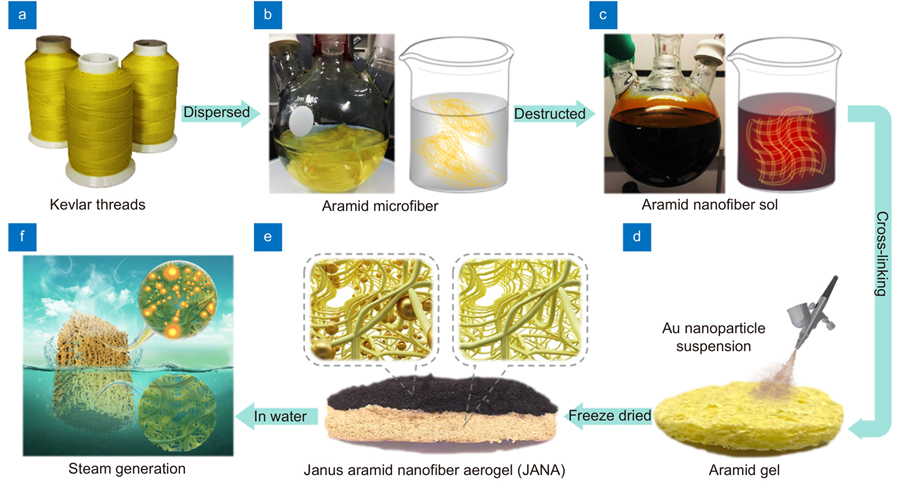
Interfacial solar steam generation (ISSG) is a novel and potential solution to global freshwater crisis. Here, based on a facile sol-gel fabrication process, we demonstrate a highly scalable Janus aramid nanofiber aerogel (JANA) as a high-efficiency ISSG device. JANA performs near-perfect broadband optical absorption, rapid photothermal conversion and effective water transportation. Owning to these features, efficient desalination of salty water and purification of municipal sewage are successfully demonstrated using JANA. In addition, benefiting from the mechanical property and chemical stability of constituent aramid nanofibers, JANA not only possesses outstanding flexibility and fire-resistance properties, but its solar steaming efficiency is also free from the influences of elastic deformations and fire treatments. We envision JANA provides a promising platform for mass-production of high-efficiency ISSG devices with supplementary capabilities of convenient transportation and long-term storage, which could further promote the realistic applications of ISSG technology.
plasmonics interfacial solar steam generation broadband optical absorption aerogel Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(5): 220061
南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院,江苏 南京 210033
超表面是由亚波长尺度的人工原子组成的二维平面超材料,具有操纵电磁波属性的能力。超表面领域的快速发展催生了多种技术/功能器件,包括超表面全息术、矢量涡旋光技术、超透镜、偏振转换器等。主动性超表面是指可以通过电、磁、光照、热、应力等外部刺激对超表面的结构、性质和功能进行灵活调控的超表面。近年来,人们一直致力于研究基于多种调控技术的多功能可调谐超表面,从而实现动态调控电磁波的目的。本文归纳总结了基于多种调控方法的可调谐超表面的研究进展,主要包括基于液晶的可调谐超表面、基于相变材料的可调谐超表面和结构可重构型可调谐超表面,并讨论了不同类型可调谐超表面的优势、面临的挑战以及未来的发展方向。
光学设计 超表面 可调性 液晶 相变材料 微纳光子学

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Hefei National Laboratory, Hefei 230088, China
3 Shishan Laboratory, Suzhou Campus of Nanjing University, Suzhou 215000, China
4 e-mail:
5 e-mail:
6 e-mail:
High-dimensional entanglement is of great importance in quantum communications and can be realized by encoding information on multiple degrees of freedom (DoFs) of the photons. Conventionally, the realization of such high-dimensional entanglement involves different combinations of bulky optical elements. In this work, we present the use of a single dielectric metasurface to generate high-dimensional entanglement by modulating multi-DoFs of photons. By sending one of the polarization-entangled photons to interact with the metasurface, we encode path, spin angular momentum, and orbital angular momentum information to the original state. We achieve a four-qubit quantum state in the experiment. To verify it, we experimentally demonstrate the nonlocal correlations between the two photons by recording the correlated images, and we also perform a quantum state tomography measurement. This scheme can be applied to on-chip quantum state manipulation, which is promising in quantum communication with integrated components.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(12): 2702
1 合肥米克光电技术有限公司,安徽 合肥 230093
2 合肥工业大学仪器科学与光电工程学院,安徽 合肥 230009
3 安徽省计量科学研究院,安徽 合肥 230051
提出了一种使用多线阵相机、双光源频闪照明成像和分布式并行图像处理技术的锂电池极片涂布涂层缺陷检测方法。该方法使用明、暗光源频闪交替照明,两台高速线扫相机在同一个位置交替分别拍摄明场和暗场图像,既提高了对缺陷的检测分辨能力,也提高了检测效率。在处理环节,该方法使用主从分布式处理架构,使用两台子处理工控机多线程并行处理各自相机的图像数据,并将获得的缺陷数据通过TCP/IP传输至上位处理工控机,进行数据融合与缺陷分类处理。实验表明,使用该方法的锂电池极片涂布检测系统可以实现在线检测,具有极高的实用价值。
机器视觉 数字图像处理 图像检测系统 并行处理 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(18): 1810006
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Water, Environment and Agriculture Product Safety, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University Changsha 410083, P. R. China
2 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, P. R. China
Near infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging guided photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a technique which has been developed in many clinical trials due to its advantage of real-time optical monitoring, specific spatiotemporal selectivity, and minimal invasiveness. For this, photosensitizers with NIR fluorescence emission and high 1O2 generation quantum yield are highly desirable. Herein, we designed and synthesized a "donor–acceptor" (D-A) structured semiconductor polymer (SP), which was then wrapped with an amphiphilic compound (Pluronicr F127) to prepare water-soluble nanoparticles (F-SP NPs). The obtained F-SP NPs exhibit good water solubility, excellent particle size stability, strong absorbance at deep red region, and strong NIR fluorescent emission characteristics. The maximal mass extinction coe±cient and fluorescence quantum yield of these F-SPs were calculated to be 21.7 L/(g·cm) and 6.5%, respectively. Moreover, the 1O2 quantum yield of 89% for F-SP NPs has been achieved under 635 nm laser irradiation, which is higher than Methylene Blue, Ce6, and PpIX. The outstanding properties of these F-SP NPs originate from their unique D-A molecular characteristic. This work should help guide the design of novel semiconductor polymer for NIR fluorescent imaging guided PDT applications.
Donor–acceptor structure semiconducting polymer nanoparticles photodynamic therapy near infrared fluorescence imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2022, 15(4): 2240006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Integration and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China.
Achromatic metalens composed of arrays of subwavelength nanostructures with spatially varying geometries is attractive for a number of optical applications. However, the limited degree of freedom in the single layer achromatic metasurface design makes it difficult to simultaneously guarantee the sufficient phase dispersion and high diffraction efficiency, which restricts the achromatic bandwidth and efficiency of metalens. Here we propose and demonstrate a high efficiency achromatic metalens with diffraction-limited focusing capability at the wavelength ranging from 1000 nm to 1700 nm. The metalens comprises two stacked nanopillar metasurfaces, by which the required focusing phase and dispersion compensation can be controlled independently. As a result, in addition to the large achromatic bandwidth, the averaged focusing efficiency of the bilayer metalens is higher than 64% at the near-infrared region. Our design opens up the possibility to obtain the required phase dispersion and efficiency simultaneously, which is of great significance to design broadband metasurface-based optical devices.Achromatic metalens composed of arrays of subwavelength nanostructures with spatially varying geometries is attractive for a number of optical applications. However, the limited degree of freedom in the single layer achromatic metasurface design makes it difficult to simultaneously guarantee the sufficient phase dispersion and high diffraction efficiency, which restricts the achromatic bandwidth and efficiency of metalens. Here we propose and demonstrate a high efficiency achromatic metalens with diffraction-limited focusing capability at the wavelength ranging from 1000 nm to 1700 nm. The metalens comprises two stacked nanopillar metasurfaces, by which the required focusing phase and dispersion compensation can be controlled independently. As a result, in addition to the large achromatic bandwidth, the averaged focusing efficiency of the bilayer metalens is higher than 64% at the near-infrared region. Our design opens up the possibility to obtain the required phase dispersion and efficiency simultaneously, which is of great significance to design broadband metasurface-based optical devices.
metalens metasurface nanostructure waveguide Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(1): 200008
Author Affiliations
Abstract
南京大学固体微结构物理国家重点实验室现代工程与应用科学学院, 南京 210093
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) have extensive application prospects in high-sensitivity biosensing because of their extraordinary optical properties. However, the large size and cost of prism-based plasmonic sensors limit their commercial applications. Fortunately, the emergence of metallic nanostructured sensors has provided an effective approach to realize low-cost and highly integrated plasmonic sensors. In this review, we first assess the current status and advantages of plasmonic nanostructured sensors, then focus on our group's recent research on their miniaturization, integration, and fabrication cost reduction. Our work is of significance for the development of both plasmonic sensing theory and nanostructured sensing technology.
表面等离子激元 纳米阵列结构 光学传感器 光学集成器件 生化传感 surface plasmon nanoarray structure optical sensor optical integrated devices biochemical sensing Journal of Semiconductors
2019, 48(1):
温州大学数理与电子信息工程学院, 浙江 温州 325035
针对传统多光谱成像颜色测量系统光谱反射率重建算法计算量大、操作繁琐耗时、成本高等缺点,提出一种由LED主动照明光源和黑白高速相机构建的多光谱成像颜色测量系统。采用多个单色LED拟合出相对光谱功率分布与相机光谱灵敏度曲线成倒数关系的照明光源,并利用黑白相机的输出响应直接重建物体的光谱反射率。实验结果表明,与分光光度计测量结果相比,该方法测量Macbeth ColorChecker 24标准色卡的光谱反射率的平均误差在2.3个CIELAB色差左右。该系统具有原理简单可行、不需要滤光片、光谱反射率重建算法简单快速等优点。
视觉光学 颜色测量 光谱反射率重建 LED光源拟合 主动照明光源 多光谱成像系统





